Tuberculosis (TB) is a chronic global disease caused by
Mycobacterium or sometimes by mycobacterium bovis and other atypical mycobacteria which are a type of bacteria.
It is one of the major health problems in the world. symptoms of tuberculosis in females are different because tuberculosis affects a lot of organs.
The main target of tuberculosis is the pulmonary system (lung) but it can also affect other parts of the body such as bone, nervous system, urinary system, or glands.
Symptoms of tuberculosis in females
A tuberculosis infection has three types of infection, symptoms of tuberculosis in females are different in each type of infection.
Primary infection
In this stage, the immune system may destroy the germs so no symptoms appear.
But maybe symptoms of tuberculosis in females are like flu symptoms such as low fever, cough, or tiredness.
No transformation of infection.
Latent infection
Immune system cells build a wall around lung tissue with tuberculosis bacteria.
The bacteria can't do any more harm if the immune system keeps them under control.
No symptoms, latent infection may be turned into active infection.
Active infection
Tuberculosis bacteria affect mainly the pulmonary system (lung).
Tuberculosis infection may be pulmonary or extrapulmonary.
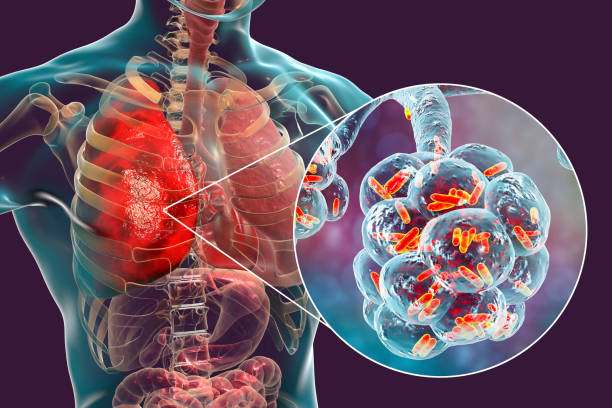
Symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis
Fever, chills, or tiredness.
Cough with mucus with yellow, or green color or bleeding. It will last three more weeks.
Pain during breathing and pain in the chest.
Sweating.
Loss of appetite.
Weight loss and in children no gain weight.
There is active tuberculosis disease in the voice box outside the lungs.
It has the same lung symptoms as tuberculosis in females.
Symptoms of extrapulmonary tuberculosis
Tuberculosis bacteria can transform into other organs through hematogenous or lymphatic routes.
It transforms into other people by breathing or sexual intercourse.
Symptoms of lymph node tuberculosis
The disease is localized to the superficial lymph nodes (anterior or posterior cervical chains) or supra clavicular, it is mostly in the neck.
In the early stage, skin is normal then changes gradually from inflammation until fistulisation.
Common symptoms of tuberculosis in females are weight loss, fever, asthenia, and night sweating.
It affects lymph nodes and compresses the bronchial tubes, causing severe cough and possibly a collapsed lung.
Swelling of one or more lymph nodes is painless and nonadhesion.
Symptoms of urinary tuberculosis
Low fever, weight loss.
Cystitis syndrome (frequent urination at night, pain at the end).
Hematuria.
Pyuria (purulent urine).
Low back pain.
Dysuria.
Symptoms of intestinal tuberculosis
Abdominal pain for a longer time, feeling tired, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, weight loss, bloating, and diarrhea may be a watery stool or blood in stool.
Ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdomen).
Hepatomegaly (enlarged liver) or jaundice.
Intestinal obstruction.
Symptoms of cardiac tuberculosis
Cardiac symptoms of tuberculosis in females are fever, malaise, cough, difficulty in breathing, chest pain, night sweats, weight loss, and right upper quadrant pain.
Swollen vein neck and difficulty breathing if it reaches the heart because it leaks fluid into the space between the pericardium and the heart and is called tuberculous pericarditis.
Symptoms of brain tuberculosis
Low fever, severe constant headache, nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, and may reach to comb.
When the immune system weakens tuberculosis reaches the brain.
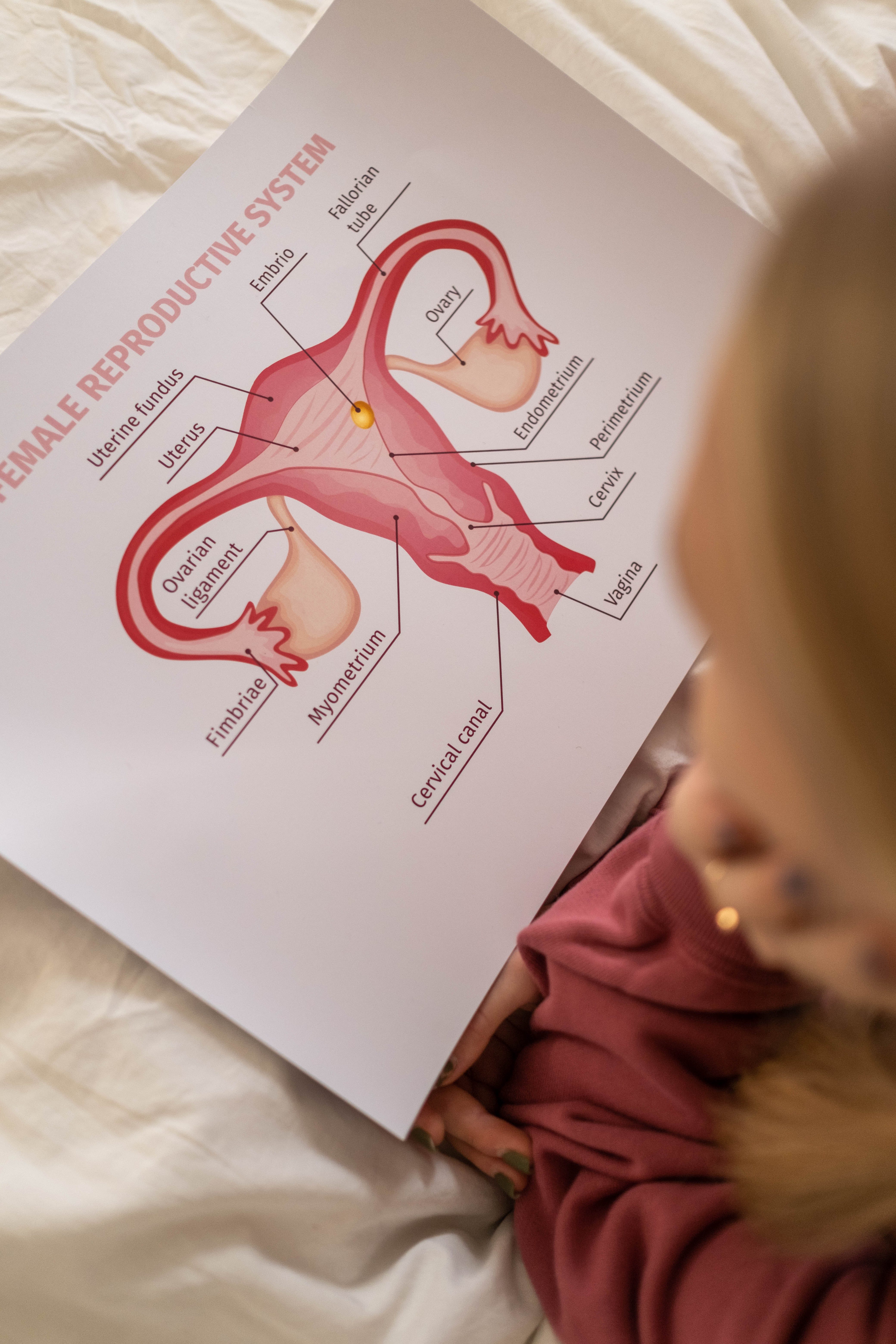
Female genital tuberculosis
Tuberculosis bacteria reach to genital system in females through pulmonary or abdominal tuberculosis, hematogenous, lymphatic route.
It affects young females from 20-45 ages, it is genital female tuberculosis which is a type of extrapulmonary tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis affects with high percent on fallopian tube or uterine endometrium with less percent or ovaries with little percent.
Some cases are without symptoms of tuberculosis in females.
Genital symptoms of tuberculosis in females are difficult to detect in the first stage.
Must be monitoring the history of genital tuberculosis in the family.
In people with weakened immune systems due to HIV/AIDS, the bacteria may also spread to other organs such as the lungs or liver.
Genital tuberculosis can transform through skin-to-skin contact with an infected person or sexual intercourse.
General symptoms of tuberculosis in females
Menstrual dysfunction (menstrual irregularities), dysmenorrhea, or postmenopausal bleeding.
Puberty menorrhagia, heavy menstrual bleeding in early stages.
Postmenopausal bleeding, oligomenorrhea or hypomenorrhoea.
Anorexia and weight loss.
Feeling unwell, always tired.
Low-grade fever or pyrexia.
Lower abdominal discomfort or pain (abdominal or pelvic pain).
Vaginal discharge (abnormal).
Dyspareunia.
Don’t get pregnant for the first time.
Presence of pelvic mass, cyst, abscess.
Infertility primary and secondary.
Swelling, and ulcers in the genital area.
Pain during urination or intercourse.
Clinical symptoms of tuberculosis in females
The clinical symptoms of tuberculosis in females depend on the site of infection.
40% of infertile women with genital tuberculosis are asymptomatic.
The most common symptoms of tuberculosis in females are infertility due to damaged fallopian tubes.
Very low endometrium receptivity, or ovarian damage with low ovarian reserve and volume.
Effect of tuberculosis on fallopian tubes (90%)
The infection makes tubes swollen, tube-ovarian masses, and dense adhesions.
This disease makes women more susceptible to ectopic pregnancy and infertility.
Loss of fallopian tube function due to ciliary damage.
Effect of tuberculosis on uterus (70%)
It causes chronic inflammation, adhesion, masses, and destruction of the endometrium.
Effect of tuberculosis on ovary (30%)
It makes adhesions, caseation, adnexal cysts, or mass formation with defective ovarian function and sometimes destruction of the ovary.
It decreased the production of progesterone.
Effect of tuberculosis on cervix (10%)
It causes more ulceration and is not easily treated.
Effect of tuberculosis on vagina and vulva (1%)
It is rare and causes ulceration.
Diagnosis
In pulmonary tuberculosis tools are chest X-ray or taking samples.
In extrapulmonary tuberculosis tools are nucleic acid, immunological test, biopsy, body fluid examination, or sputum acid-fast bacillus.
In female genital tuberculosis tools are endometrial samples or a laparoscopy with hysteroscopy.
Diagnosis is a difficult process because tuberculosis is a silent disease, asymptomatic, misdiagnosed (similar to a lot of diseases), and difficult to take samples.
Summary
All of these symptoms do not prove tuberculosis infection.
Symptoms of tuberculosis in females are similar to symptoms of lots of diseases.
So there must be physical examinations like lymphadenopathy (lymph node TB), bones and joints (skeletal TB), chest X-ray (pulmonary TB), abdominal examination (abdominal TB), and gynecological examination if no history of the disease.

You must be logged in to post a comment.