Ovarian cancer tumor is a malignant type of tumor of the ovaries or the fallopian tubes.
It happens when ovarian cells or nearby cells develop mutations in their DNA. This leads to rapid and multiple cell growth, forming a tumor (mass) of cancer tissue.
Ovarian Tumors in general may be benign (not cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), both types occur when ovarian or fallopian tube cells abnormally and excessively grow and divide to form a mass.
The difference between them is the behavioral changes of the cells in the malignant type.
In this article, we will concentrate on the malignant type characterized by changes in the number, function, and consistency of the cells.
The ovarian cancer tumor is serious because of its quick growth and progression from early to advanced stages within one year.
Metastasis (spread of the tumor to the nearby organs) is mainly inevitable in ovarian cancer tumor, especially if the diagnosis is late (after 8 months or more).

Aetiology and risk factors of ovarian cancer tumor
There are no definite causes for ovarian cancer tumor discovered till now, although there are many risk factors for its incidence.
Here are the most high-risk factors for it :
- Inherited faulty genes, such as BRCA genes or genes of Lynch syndrome.
- Using HRT (hormonal replacement therapy).
- Early period starting age or late menopause (over 50-55) or haven't been pregnant before, because this means having long periods of hormonal production due to multiple ovulation.
- Family history of ovarian cancer tumor.
- Endometriosis.
- Smoking.
- Obesity.
- Diabetes.
- Old age.
- Exposure to some agents such as pesticides, herbicides, and talc.
Symptoms and signs of ovarian cancer tumor
Like a lot of cancers, ovarian cancer tumor may have no specific symptoms or signs, and they are vague in diagnosing the cancer.
It may also have been discovered lately because it lacks symptoms or signs, so we call it the “silent killer.”
They will be significant and warning if they start to be daily and never go away themselves, although this may occur too late to diagnose and treat the disease.
Only about 20% of ovarian cancer tumor cases are discovered early enough to be treated.
These are the symptoms and signs every woman should observe if they are persistent and don't go away themselves :
- Abdominal pain.
- Pelvic pain.
- Stomach upset.
- Alter appetite, feeling full after eating a smaller amount than usual.
- Anorexia.
- Alter urination habit (urgency or frequency or both).
- Constipation.
- Back pain.
- Fatigue.
- Alter periods of the patient (heavier bleeding or irregular than normal).
- Belly swelling.
- Bloating (feeling of uncomfortable fullness).
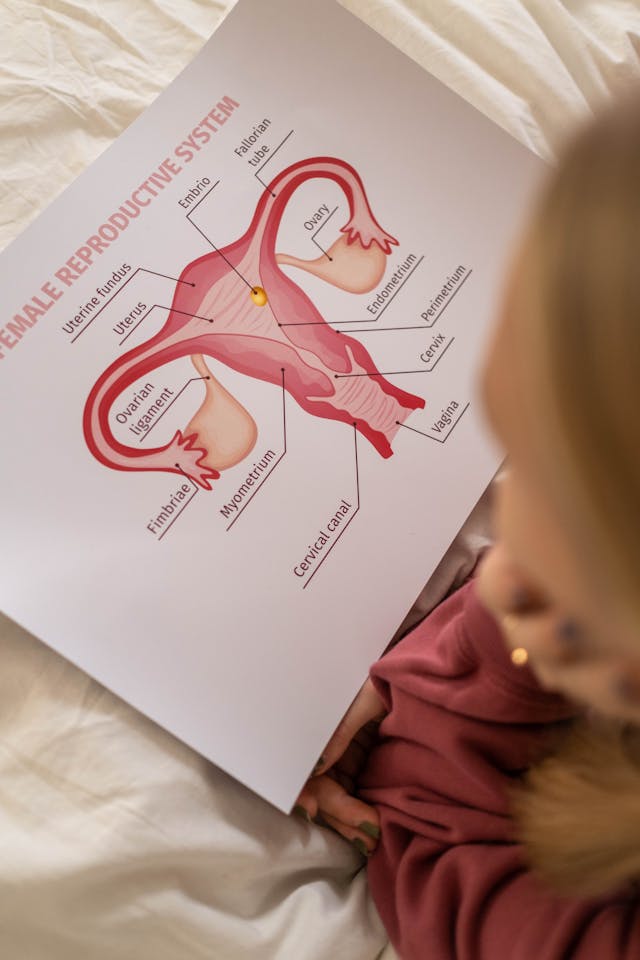
Types of Ovarian Tumors
Classification of ovarian cancers is based on the types of cells they originated from.
The 3 cell types are :
1- Epithelial cells:
They cover the outer lining of ovarian tissue, from which most ovarian cancers originate.
2- Germ cells:
They are the producer cells of ova (eggs), and some ovarian cancers form in these cells.
3- Sex cord-stromal cells:
These are the cells that provide the structural form of the ovary.
They are also responsible for sex hormones production (estrogens and androgens).
Some of the ovarian cancers formed in these cells.
Thus the ovarian cancer tumor types are :
Epithelial ovarian carcinomas
These are the most common type of ovarian cancer tumor.
85% to 90% of these cancers involve the outer surface of the ovary cells.
This type includes many subtypes such as mucinous and serous carcinomas.
They mimic fallopian tube cancer and primary peritoneal cancer.
Mainly, they spread first to the lining tissues, pelvic organs, and abdomen, then to the rest of the body.
This type is diagnosed in advanced stages in about 70% of cases.
Germ cell ovarian tumors
This type is rare (less than 2% of ovarian cancers), they begin in the female reproductive cells that are ova.
They usually affect young women up to early 30’s, about 90% of patients can survive for 5 years after the diagnosis.
The most common subtype is ovarian teratoma.
Sex cord-stromal ovarian tumors
They represent about 1% of all ovarian carcinomas, They may be malignant or benign tumors.
These types of tumors are formed in the supportive tissue of the ovaries.
Often discovered in the early stages.
Pervaginal bleeding is the most common presentation of these types.
Granulosa sex cord-stromal tumors are the most common subtype.
Borderline ovarian tumors
These are abnormal masses of cells that form in the covering tissue of the ovaries.
They aren’t considered cancers and are usually treated by surgery.

Grading and staging of ovarian cancers
To grade a tumor means knowing the nature of the cancer cells, according to how they are similar to normal ones in their differentiation. Thus, their behavior and rate of growth and spread are predicted.
TNM staging of ovarian cancer tumor represents the characteristic features of it, the spread of the tumor to the nearby lymph nodes, and if there is metastasis to other organs.
These classifications are important to identify the proper treatment and to predict the prognosis.
There are 3 grades and 4 stages of ovarian cancer tumor :
Grade 1
The cancer cells are still well-differentiated and similar to the normal cells.
At this grade, the cancer is less likely to spread or recur after treatment.
Grade 2
The cancer cells are moderately differentiated and start to differ from the normal ones.
Spread is also less likely to occur but its chance is present.
Grade 3
The cancer cells are poorly differentiated and very different from the normal ones.
The spread danger and recurrence of cancer after treatment is very high.
Stage 1
The cancer is limited to the ovaries (one of them or both) or the fallopian tubes.
There is no further spread.
Stage 2
Cancer cells are localized in the ovaries (one of them or both) or the fallopian tubes and some of them have reached the pelvis, but there is no cancer outside the pelvis.
According to sites of spread, this stage is classified as stage 2A and stage 2B.
Stage 3
Cancer cells are present in the ovaries (one of them or both) or the fallopian tubes and have also spread outside the pelvis to the lymph nodes at the back of the abdomen and/or to the abdomen.
According to sites of spread, this stage is classified as stages 3A, 3B, and 3C.
Stage 4
Cancer now has spread outside the abdomen and the pelvis to other organs like the lungs/spleen/liver/lymph nodes further away and even the bone.
According to sites of spread, this stage is classified as stage 4A and stage 4B.
How is an ovarian cancer tumor diagnosed?
Many tests and imaging can detect the presence of ovarian cancer and its grade and stage as :
Imaging work up
- The most often used imaging for screening of ovarian cancer tumor is transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS).
- CT abdomen and pelvis with contrast:
It is very important in diagnosis, but PET/CT is the technique of choice for the detection of the lesion and treatment follow-up.
- Brain and spinal cord MRI with contrast:
Multiple cross-section pictures are helpful in metastasis detection.
- Chest x-ray:
For metastasis detection in the lungs.
- Barium enema x-ray:
For detection of cancer invasion to the colon or rectum, but colonoscopy may be done instead.
- Laparoscopy.
- Colonoscopy.
Biopsy
It is a procedure of removing a piece of an ovarian tumor and examining it to determine certainly if it is a cancer.
It is commonly done when removing the tumor during surgery.
In a few cases, the suspected ovarian cancer tumor may be tested by taking a biopsy during laparoscopy.
Also, the biopsy can be taken by using a needle directly placed into the tumor through the abdominal skin guided by ultrasound or CT scan.
This is only done when the surgery can’t be done in the advanced stages of cancer to avoid the possibility of cancer spreading.
If there is ascites (collection of fluid in the abdominal cavity) or pleural effusion (collection of fluid in the chest),
samples are taken from these fluids through a procedure called “paracentesis” and examined by a pathologist with the other biopsy in the lab.
Lab tests
- CA-125 test:
It is a protein measured in blood and Its level is elevated in ovarian cancer tumor (more than 45U/ml) may indicate cancer possibility.
It is an important diagnostic tumor marker for ovarian cancers.
- CA19-9 or HE4:
Other markers may be used if CA-125 is at a normal level.
- Human chorionic (HCG).
- Alfa feto protein (AFP).
- Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH).
- Complete blood count (CBC):
White blood cell (WBC) levels are typically elevated in ovarian cancer tumor.
The treatment strategy for ovarian cancer tumor
This will depend on :
- Tumor size.
- Tumor site.
- Tumor spread (metastasis).
- General health of the patient.
Mainly cancer treatments are surgery and chemotherapy, other treatments such as hormonal treatment and targeted medicines are included.
Other treatments like immunotherapy and palliative treatment are used.
Surgery
The operation type depends on cancer nature and its stage and grade.
The prognosis (effect of treatment) is better if the ovarian cancer tumor is diagnosed early.
- In early stages (no metastasis) :
One or Both ovaries (according to the localization of cancer) and fallopian tube/s are removed (unilateral or bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy).
The cervix and uterus are also removed by abdominal hysterectomy.
- In late stages (there is metastasis) :
Surgery to remove as much of the cancer tissue as possible is done and this may include parts of the bowel removal.
Chemotherapy
These are chemical drugs used to kill malignant (cancer) cells which are fast-growing.
Chemotherapy drugs are taken either orally or through intravenous injection.
Chemotherapy is usually taken after surgical operations to kill any remaining cancer cells.
Targeted therapy
This means focusing on previously determined weaknesses concerning cancer cells.
The targeted drugs can kill cancer cells by attacking their weaknesses.
Hormone therapy
This means using anti-estrogen drugs to block its effects on cancer cells, thus stopping their growth.
This strategy is more effective in slowly growing ovarian cancer tumor and recurrent cases after surgery and chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy
These are drugs induced to stimulate the immune system to fight cancer and kill its cells.
Immunotherapy is an option in specific situations.
Palliative (supportive) treatment
This is not only medication but also a whole plan working together with other treatments.
When palliative treatment is used parallel with all other treatment plans, patients with ovarian cancer tumor feel better and their survival rate is increased.
This includes drugs for pain relief and other symptomatic medications for serious illness.
Also, psychiatric consultation is necessary to provide psychic support to the patients.
Palliative care is better used while undergoing other aggressive treatments (surgery and chemotherapy).

How to prevent ovarian cancer tumor?
Unfortunately, there is no definite way to prevent ovarian cancer tumor, but in addition to fulfilling a healthy lifestyle, caring for your diet and weight and practicing sports, there are some ways that can still help you reduce your risk such as :
Pregnancy
The more full-term pregnancies you have had the lower ovarian cancer risk for you.
Tubal ligation
If you get your fallopian tubes tied, this puts you at a lower risk of having ovarian cancer tumor.
Notice that you shouldn’t do that to lower the risk of having ovarian cancer, but only do that if you intend to prevent pregnancy as well.
Taking contraceptive pills
Consider using birth control pills after asking your specialist whether they are suitable for you or not, because they have other risks to your health in specific conditions.
Taking contraceptive pills does reduce ovarian cancer risk.
Talk to your doctor if you are one of the high-risk group
If you have a family history or a possibility of inherited faulty genes or any other risk factors from those we discussed, you should talk to your doctor about it.
The doctor can determine the concerns of your risk factors and their effects on your probability of having an ovarian cancer tumor.
In conclusion :
Ovarian cancer tumor is a malignant type of tumor of the female genital system with various types.
It has no definite causes but has some risk factors to keep an eye on.
Its symptoms and signs are vague and not characteristic especially in early cases, making the diagnosis to be missed or late.
Ovarian cancer tumor has grades according to the differentiation of cancer cells and stages according to some factors but the most important one is metastasis.
To diagnose an ovarian cancer tumor there are many investigations and imaging should be done but the gold standard in diagnosis is biopsy and CA-125 blood level.
The treatment strategies are different according to definite factors like the stage in which the cancer is and if there is metastasis.
Prevention of having an ovarian cancer tumor is not inevitable but there are many ways to minimize the possibility of its occurrence.
Read more about :

You must be logged in to post a comment.